Payment Type:T/T,Others
Incoterm:FOB,CFR,CIF,EXW,DDP,DDU,Express Delivery
Transportation:Ocean,Land,Air,Express,Others
Port:Guangzhou,Shenzhen,Ningbo
$0.0310000-99999Piece/Pieces
$0.02≥100000Piece/Pieces
Model No.: 18*6*6mm
Brand: YB
Place Of Origin: China
Species: Permanent
Composition: Plastic Magnet, Neodymium Magnet, Ferrite Magnet, Rare Earth Magnet, Ndfeb Magnet, Alnico Magnet, Rubber Magnet
Shape: Bar, Stick, Strip, Cup Shape, Block, Coil, Ball, Pot / Cup Shape, Sheet
Application: Moto Magnet
Tolerance: ±1%
Processing Service: Bending, Welding, Decoiling, Cutting, Punching, Moulding
Product Name: Ferrite Magnet for stepper motor
Material Grade: Y10T
Color: original color
Quality Certificate: CE,ROHS,MSDS
Certificate: ISO9001
Delivery Time: 7-15 days
Brand: YB
Packaging: Carton package and then packed in pallets
Productivity: 30000000pcs per month
Transportation: Ocean,Land,Air,Express,Others
Place of Origin: China
Supply Ability: 30000000pcs per month
Certificate: ISO9001
HS Code: 8505190090
Port: Guangzhou,Shenzhen,Ningbo
Payment Type: T/T,Others
Incoterm: FOB,CFR,CIF,EXW,DDP,DDU,Express Delivery
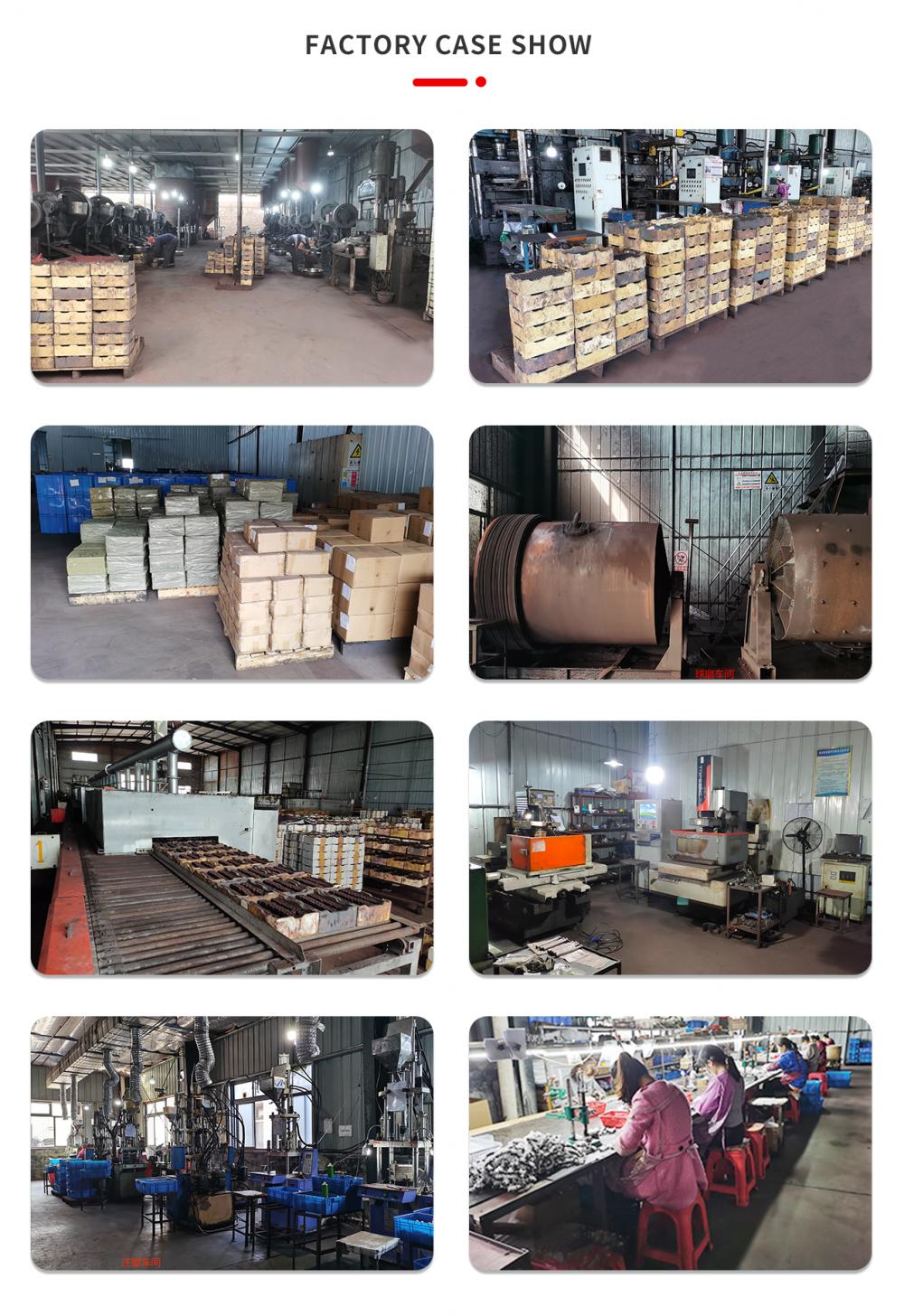
The production process of ferrite permanent magnets involves several steps:
1. Raw material preparation: The main raw materials used in ferrite magnet production are iron oxide (Fe2O3) and strontium carbonate (SrCO3) or barium carbonate (BaCO3). These materials are carefully selected and mixed in the desired proportions to form a homogeneous powder.
2. Mixing: The mixed powder is then subjected to a milling process to ensure a uniform distribution of particles and to break up any agglomerates. This step is crucial for achieving the desired magnetic properties.
3. Forming: The milled powder is then pressed into the desired shape using a hydraulic press. The pressing process involves applying pressure to the powder inside a mold to form a compacted shape. The pressure applied determines the final density and strength of the magnet.
4. Sintering: The compacted shapes are then subjected to a sintering process, where they are heated in a furnace at high temperatures (typically around 1200-1400°C). During sintering, the particles fuse together, resulting in a solid and dense magnet. The sintering process also helps in aligning the magnetic domains within the magnet, which enhances its magnetic properties.
5. Machining and finishing: After sintering, the magnets are often machined to achieve the desired dimensions and tolerances. This may involve cutting, grinding, or drilling the magnet to its final shape. The magnets are then cleaned and coated with protective materials like epoxy or nickel to prevent corrosion.
6. Magnetization: The final step in the production process is magnetization. The magnets are subjected to a strong magnetic field, either by passing an electric current through a coil or using a permanent magnet. This aligns the magnetic domains within the magnet, resulting in a magnetized product.
Once the production process is complete, the ferrite permanent magnets are ready to be used in various applications, such as electric motors, speakers, magnetic separators, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines.